O' Shea说道,“我们知道对大多数人而言,一旦体重增加,就很难减掉。吃少些,多活动,体重将会减轻,这未免太简单化了。实际情形并不是这样的。人体有一种非常强大的反应来防止体重减轻,如今我们知道这涉及免疫系统。”
“我们通常认为免疫系统的作用就是抵抗感染和疾病。然而,从进化的角度来说,突然或快速的体重减轻可能是生存的一种更加直接的威胁。这种免疫系统反应产生的一种后果是尽管采取最好的努力来控制卡路里摄入和进行锻炼,人们还需努力减轻体重。我们的发现对其中的原因提供一种更好的理解,而且它们解释了免疫系统在调节体重中发挥的动态作用。”
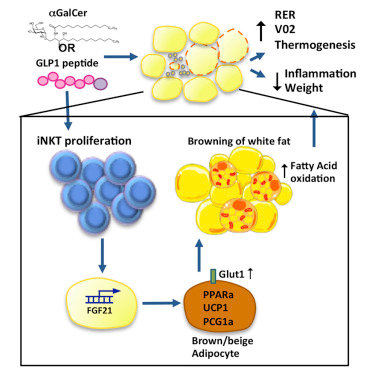
Lynch解释道,“我们发现一种非常常见的被称作不变自然杀伤T细胞(invariant natural killer T cell, iNKT细胞)的免疫细胞在发起一系列复杂的调节和加强体重减轻的事件中发挥着关键性作用。”
“这种iNKT细胞是协助脂肪细胞表达一种被称作成纤维细胞生长因子-21(fibroblast growth factor-21, FGF-21)的小分子蛋白所需的,其中FGF-21触发人体进行代谢,或者说将白色脂肪转化为一种更加健康的棕色脂肪。白色脂肪棕色化消耗大量能量,导致增加的代谢率和体重减轻。”
“我们知道肥胖的人经常具有反应缓慢的免疫系统和较低水平的iNKT细胞。当iNKT细胞较少时,人体就不能产生FGF-21,这就会阻止人体将白色脂肪转化为棕色脂肪。”
“因此,如果你刺激人体产生iNKT细胞,那么你能够增加FGF-21的数量。这接着导致白色脂肪更多地发生棕色化,和增加的代谢率和体重减轻。”
“这种新的知识为治疗体重减轻提供新的途径,将极大地加强我们改善现存的治疗体重减轻的激素疗法的能力。”
O' Shea认为这些发现代表着我们理解为何人们在付出极大努力后经常发现减轻体重为何如何困难方面取得重大进展。
“这些发现应当有助破解与肥胖相关的很多谜团,而且最为重要的是,它们可能显著地改善病人的治疗结果。最终,这项研究强调了在第一时间预防体重增加的极端重要性。这项研究应当有助政策制定者优先考虑肥胖预防策略,特别是儿童肥胖。”
本文系生物谷原创编译整理,欢迎转载!点击 获取授权 。更多资讯请下载生物谷APP。
iNKT Cells Induce FGF21 for Thermogenesis and Are Required for Maximal Weight Loss in GLP1 Therapy
Lydia Lynch, Andrew E. Hogan, Danielle Duquette, Chantel Lester, Alexander Banks, Katherine LeClair, David E. Cohen, Abhisek Ghosh, Bing Lu, Michelle Corrigan, Darko Stevanovic, Eleftheria Maratos-Flier, Daniel J. Drucker, Donal O’Shea, Michael Brenner
doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.003
PMC:
PMID:
Adipose-resident invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells are key players in metabolic regulation. iNKT cells are innate lipid sensors, and their activation, using their prototypic ligand α-galactosylceramide (αGalCer), induces weight loss and restores glycemic control in obesity. Here, iNKT activation induced fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) production and thermogenic browning of white fat. Complete metabolic analysis revealed that iNKT cell activation induced increased body temperature, V02, VC02, and fatty acid oxidation, without affecting food intake or activity. FGF21 induction played a major role in iNKT cell-induced weight loss, as FGF21 null mice lost significantly less weight after αGalCer treatment. The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, liraglutide, also activated iNKT cells in humans and mice. In iNKT-deficient mice, liraglutide promoted satiety but failed to induce FGF21, resulting in less weight loss. These findings reveal an iNKT cell-FGF21 axis that defines a new immune-mediated pathway that could be targeted for glycemic control and weight regulation.
相关会议推荐

2016 下一代CAR&TCR-T研讨会
会议时间:2016.10.21-2016.10.22 会议地点:上海